Trade Restrictions
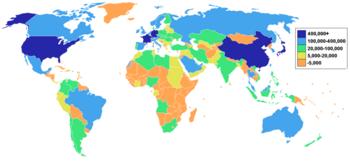
Caption: This map shows exports in millions of dollars. The U.S., France, Germany, China, and Japan are the largest exporters; the United States exported over $1.4 trillion of goods in 2006.
Free, open trade between countries is important to healthy economies. It allows companies and workers to specialize in what they do best. Competition forces companies to be more productive. Costs are kept lower. Consumers have the options of buying cheaper and better goods and services. Free trade helps create jobs, both in the domestic country where goods are made and in the foreign country where the goods are imported.
In spite of the many advantages of free trade, many nations put limits on trade for a variety of reasons. The main types of trade restrictions are tariffs, subsidies, quotas, embargoes, licensing requirements, and standards.
A tariff is a tax on goods imported from a foreign country. Tariffs raise the price of the imported goods. This makes the price of the imported goods equal to or higher than the price of the domestic goods. The government of the country that is importing the goods collects the money from the tariff. Remember that a tariff on tea led to the American Revolution!