Government and Money
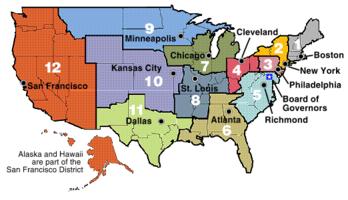
Caption: This is a map showing the districts of the twelve Federal Reserve Banks.
The United States is a big country. The American government spends a great deal of money to run the country. The Federal Reserve System is the government's bank. It is divided into twelve regional banks across the country, with its main headquarters in Washington, D.C. The "Fed," as it is commonly called, controls the amount of money in circulation. It holds a percentage of the deposits of commercial banks and lends money to them when they need it.
The Fed acts like a traffic cop. When the Fed sees there is too much traffic, or money in the economy, it slows the economy down. The Fed can require banks to put more money in reserve- that's money that cannot be loaned. Or the Fed can cause banks to raise the interest rates on loans to customers. The more interest the banks charge, the fewer the number of people who want to borrow money. People have less to spend, so the amount of money in circulation decreases.
When there is not enough money in circulation, the Fed allows banks to keep less money in reserve. The banks then have more money to lend and can lower their interest rates to encourage customers to borrow more money.