Fault-Block Mountains and Valleys
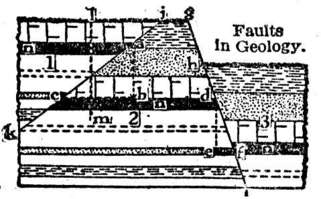
A fault is a crack in a rock. We usually associate faults with earthquakes. But did you know that faults could also form mountains?
Mountains are formed by processes called orogeny. This process usually takes place near plate boundaries. Movements at these boundaries place stress and tension on the crustal rocks. They are deformed by folding and faulting. Mountains are classified by the way they are formed.
Tensions at plate boundaries often form faults in the earth's crust. There are different types of faults. Normal faults are caused by horizontal tension. Part of the crust is uplifted, and part of it moves downward. This happens at the line where the rock is broken, called the fault plane. In an area where there are many faults, mountain ranges can form. These mountains are called fault-block mountains.
Fault-block mountains often occur where plates are moving apart. The movement causes the rocks to be stretched. Temperatures are low and the rocks are brittle. Instead of folding, they break into large blocks.
Faulting causes some sections of the rock to be uplifted. These are called horsts. A horst is a part of the earth's crust that lies between two faults. It is higher than the surrounding land.