
Worksheets and No Prep Teaching Resources
Reading Comprehension Worksheets
Nervous System
Nervous System
 Worksheets and No Prep Teaching Resources Reading Comprehension Worksheets Nervous System |
 Nervous System |
| edHelper's suggested reading level: | grades 4 to 6 | |
| Flesch-Kincaid grade level: | 8.57 |
|
Brain Waves
By Jennifer Kenny |

|
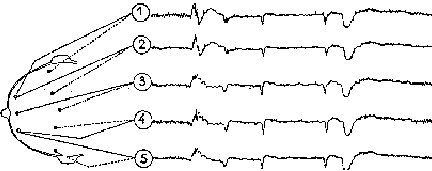 1 Each time an impulse, or a message transmitted along nerve cells, travels along a nerve, a small amount of electricity is generated. The brain itself uses power equal to a 10-watt bulb. The electrical patterns that are produced by the brain's nerve actions are called brain waves. How is this possible? Well, the human body is actually made of water, minerals, and salts, making it a good conductor of electricity. That's also why you shouldn't touch power lines or play with electrical sockets.
1 Each time an impulse, or a message transmitted along nerve cells, travels along a nerve, a small amount of electricity is generated. The brain itself uses power equal to a 10-watt bulb. The electrical patterns that are produced by the brain's nerve actions are called brain waves. How is this possible? Well, the human body is actually made of water, minerals, and salts, making it a good conductor of electricity. That's also why you shouldn't touch power lines or play with electrical sockets. |
Create Weekly Reading Books
Prepare for an entire week at once! |
| Leave your feedback on Brain Waves (use this link if you found an error in the story) |
 |
Nervous System
|